| Classification and layer detection of OCT images | ||||
|
1. Method for optical coherence tomography image classification using local features and earth mover's distance
Optical coherence tomography (OCT) is a recent imaging method that allows high-resolution, cross-sectional imaging through tissues and materials. Over the past 18 years, OCT has been successfully used in disease diagnosis, biomedical research, material evaluation, and many other domains. As OCT is a recent imaging method, until now surgeons have limited experience using it. In addition, the number of images obtained from the imaging device is too large, so we need an automated method to analyze them. We propose a novel method for automated classification of OCT images based on local features and earth mover's distance(EMD). We evaluated our algorithm using an OCT image set which contains two kinds of skin images, normal skin and nevus flammeus. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our method, which achieved classification accuracy of 0.97 for an EMD+KNN scheme and 0.99 for an EMD+SVM (support vector machine) scheme, much higher than the previous method. Our approach is especially suitable for non-homogeneous images and could be applied to a wide range of OCT images. |
||||
|
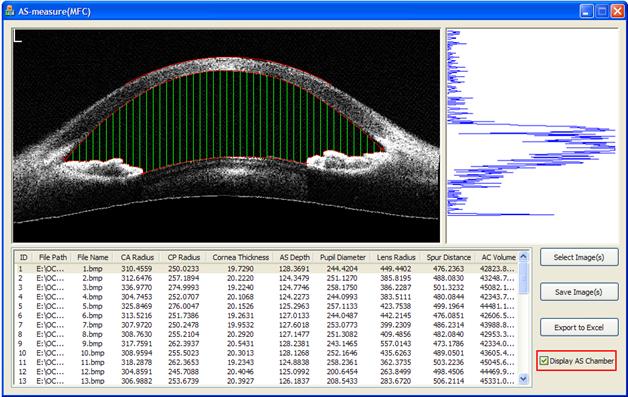
2. Automatic Extraction of the Inner Contour of the Anterior Chamber Using Optical Coherence Tomography Images
We propose an automatic extraction of the inner contour of the anterior chamber using optical coherence tomography images. Based our new method, we develop an anterior segment analysis system with GUI, which is implemented by C++. Using this system, OCT images of anterior segment could be analyzed automatically, the segment result and quantitative parameters could be viewed easily. Besides, A-Scans of the OCT images could be also analyzed by the system. The processing system is automatic, real-time and robust. |
||||
|
||||
|
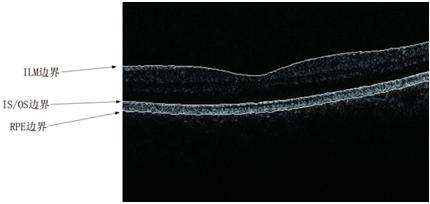
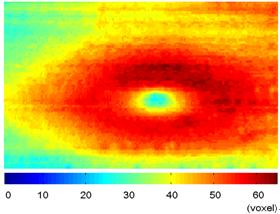
3. A new 3D segmentation method for retinal optical coherence tomography data
Retinal OCT data are seeing increasing use in diagnosing of numerous diseases, e.g. glaucoma, and an automatic 3D segmentation method for retinal OCT data is a hot topic during recent years. We present a new 3D segmentation method, based on the specific characteristics of each boundary, designing a specific calculator, to get a new volume data as the foundation of getting discrete boundary points, and then the smoothed boundary surface can be obtained after removing a small quantity of error points. Our experiments show that this method is efficient, accurate, robust, and easily expandable. |
||||
|
||||
|
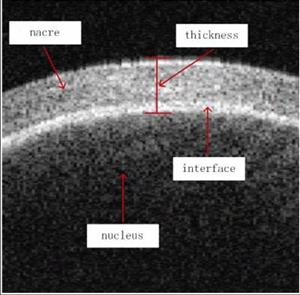
4. Automated thickness measurements of nacre from optical coherence tomography using polar transform and probability density projection
We present a novel method for automated thickness measurements of nacre from optical coherence tomography (OCT) using polar transform and probability density projection. Our method detects the upper boundary of nacre and the raw boundary is fitted to a circle by a priori. Then polar transform is applied to the image according to the fitted circle. At the following stage, we extract the lower boundary by a transform incorporating unilateral difference and intensity of pixels. Finally, we get the probability distribution of nacre thickness by probability density projection. The proposed approach was evaluated using a large number of pearl optical coherence tomography images and achieved high accuracy, which could meet the requirements of practical applications. Besides, our method is robust to noise, boundary discontinuity, and it is real time. It has potential to be used in processing of some other OCT images with circle-like boundary. |
||||
|
||||
| References: | ||||
|
||||
| [ 返回 ] | ||||
|
|
||||